










 |
          |
When the modulus m is prime, (usually very close to a power of 2
such as a Mersenne prime, ![]() , so that the operation of taking
the modulus will be faster) a method based on using the multiplier,
a, as the parameter to generate many sequences has been proposed.
We start with a reference value of a and choose the multiplier for
the jth stream as
, so that the operation of taking
the modulus will be faster) a method based on using the multiplier,
a, as the parameter to generate many sequences has been proposed.
We start with a reference value of a and choose the multiplier for
the jth stream as ![]() where
where ![]() is the
jth integer relatively prime to m-1. This is closely related to
the leapfrog method method discussed earlier. Conditions on a and
efficient algorithms for computing
is the
jth integer relatively prime to m-1. This is closely related to
the leapfrog method method discussed earlier. Conditions on a and
efficient algorithms for computing ![]() can be found in a recent
work of one of the authors [16].
can be found in a recent
work of one of the authors [16].
The scheme given above can be justified based on exponential sums,
which is explained in section 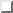 . Two
important open questions remain: (1) is it more efficient overall to
choose m to be amenable to fast modular multiplication or fast
calculation of the jth integer relatively prime to m-1, and (2)
does the good inter-stream correlation also ensure good intra-stream
independence via the spectral test?
. Two
important open questions remain: (1) is it more efficient overall to
choose m to be amenable to fast modular multiplication or fast
calculation of the jth integer relatively prime to m-1, and (2)
does the good inter-stream correlation also ensure good intra-stream
independence via the spectral test?
![]()
The National Center for Supercomputing Applications
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
ashoks@ncsa.uiuc.edu
Last modified: September 16, 1997